Publications
Dip-steered Seismic Attributes and Petrophysics Analysis for Volcanic Reservoir Characterisation: A Case Study of Kora Volcano, New Zealand
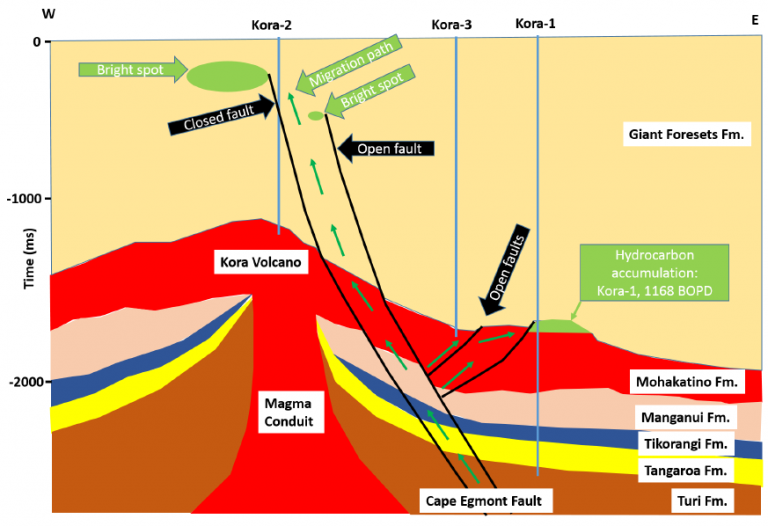
Kora Volcano is a submarine stratovolcano that is located in Northern Taranaki Basin, New Zealand. Volcanism associated with the formation of Kora Volcano is suggested as the main factors that control the hydrocarbon prospect in this area. This study aimed on characterising volcanic reservoirs that structurally and stratigraphically complex. 3D seismic cube and well data were used to characterise the reservoir by performing seismic attributes and petrophysics analysis.
Seismic attributes were generated from seismic data and accounted the local dipping and azimuth of the reflectors, known as dip-steering. Significant enhancement after the application of dip-steering in generating seismic attributes to delineate the complex structural framework suggested that the method is extremely important in modern seismic attributes analysis. Also, seismic interpretation accuracy was improved significantly by using dip-steered attributes as the guidance to define the complex structures. Last, combined with petrophysics analysis, these advanced seismic attributes were used to regulate the reservoir properties distribution in seismic data.
Geologically plausible model was produced that accounted not only petrophysics parameters, but also the influence of the structures that could be an alternative way for reservoir characterisation in highly sparse well data.
Read More...